By energy, we mean that physical quantity that measures the ability of a body or a physical system to do work, regardless of whether this work is or can actually be done. The fundamental theory of energy is that it is neither formed nor destroyed, but rather changes form. In fact, energy tends to pass from one form to another, so the various energy types do not perpetually remain such but are transformed into each other. Speaking of concrete examples, chemical energy is often transformed into heat and sometimes (as in the case of the battery) into electrical energy, nuclear energy and mechanical energy spontaneously transform into heat.
The energy conversion can take place by means of special systems or in spontaneous form. From the point of view of physics, energy is important for the formulation of many theories, from classical mechanics to thermodynamics, from the theory of relativity to quantum mechanics. From the technological point of view, on the other hand, energy allows the transformation of raw materials into final products or goods or directly the supply of services useful to man and society, through the industrial system.
Energy Types
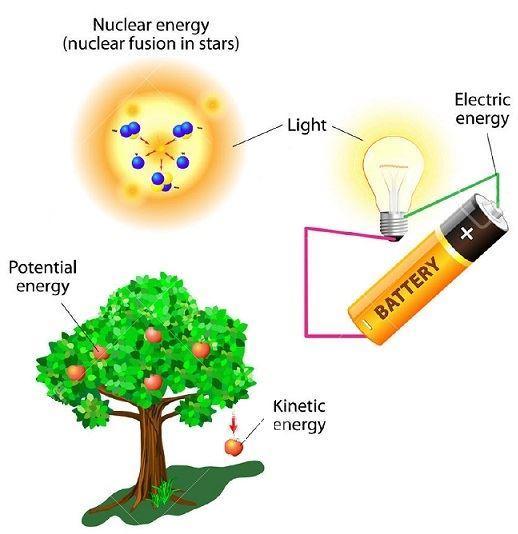
We can classify energy into two broad categories:
Potential Energy, which relates to any energy types that can be stored. We refer, for example, to the nuclear, gravitational or mechanical one
Kinetic Energy, which regards bodies in motion. For example, a flying plane or a crashing meteor has kinetic energy which is an energy type.
Potential Energy Types
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is the potential energy types that an object gains due to the gravitational effect of another object (generally very large bodies such as the Earth). This energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and the size of the attracted mass. The magnitude of the attracted mass creates the acceleration of gravity. This acceleration for the Earth is approximately 9.8 m / s² at the surface of the Earth. Gravitational potential energy is equivalent to the energy needed to place an object at a certain height. The force of gravity exerts a force that pushes the car down. During the descent, the energy is transformed into kinetic energy.
Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in the ability of a body to return to its natural position. These energy types are also called spring energy or elastic potential energy. Elasticity is a property of certain materials by which, once deformed, stretched or separated from their initial position, they can regain their original state or balance.
An (ideal) linear spring with spring constant k that is drawn (or pushed) a distance Δl has an increase in spring energy of. Electric potential energy is potential energy that results from conservative Coulomb forces. This energy is associated with the configuration of several point charges in a defined system.
Chemical Potential Energy
Chemical bonds are capable of storing potential energy. The Chemical potential energy is related to the structural arrangement of atoms or molecules. This arrangement can be the result of chemical bonds within a molecule or otherwise. The chemical energy can be transformed into other energy types through a chemical reaction. When a fuel is burned, the chemical energy is converted into heat. The metabolized food in a biological organism is transformed into energy. Through this process, green plants transform solar energy into chemical energy. Electrical energy can be converted into chemical energy through electrochemical reactions. These reactions do occur during battery charging.
Kinetic Energy
Internal Energy
Internal energy manifests itself from temperature. The warmer a body is, the more internal energy it will have. Internal energy is defined as the energy associated with the random and disorderly motion of molecules. It is on a separate scale from the ordered macroscopic energy, which is associated with moving objects. It refers to the invisible microscopic energy of the atomic and molecular scale. For example, a glass of water at room temperature on a table has no apparent energy, either potential or kinetic. If the water were thrown across the room, this microscopic energy would not necessarily be changed by the superimposition of a large-scale orderly motion on the water as a whole.
Sound Energy
Sound Energy is the energy present in a sound wave. Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves (compression/rarity). Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate – energy is transferred through the substance in a wave. Normally, the energy in the sound is much less than other forms of energy. sound energy is an energy type that is associated with vibrations of matter. It is a type of mechanical wave that means that it requires an object to travel. This object includes air and water. Sound originates from vibrations that result after an object applies force to another object.
Sound energy is the energy produced by sound vibrations when travelling by air, water or any other space. These vibrations cause pressure waves that, from the point of view of physics, lead to some level of compression and rarefaction; in other words, they amplify, jump and move as they travel from their origin to people or animal ears, which turn them into noise at different levels. This type of energy is a form of mechanical energy.
It is not contained in discrete particles and is not related to any chemical changes, but is purely related to the pressure that its vibrations cause. Most people and animals can register this type of energy with their ears and it is quite easy to identify, but it is generally much more difficult to take advantage of and although it may seem really penetrating, it does not actually produce much usable production in most cases. For this reason, sound-related energy is not normally used for electricity or other human energy needs.
Electric Power
When two points have a potential difference and are connected through an electrical conductor, what we know as electrical energy is generated, related to electrical current. The electrical power is caused by the movement of electric charges inside conductive materials. That is, each time the switch of our lamp is activated, an electrical circuit is closed and the movement of electrons is generated through metal cables, such as copper. In addition to metal, for this transport to exist and a light bulb to be lit, a generator or battery is necessary to drive the movement of electrons in a given direction.
Thermal Energy
It is associated with the amount of energy that passes from a hot body to a colder one, manifesting itself through heat. Thermal energy (also heat energy or heat energy) is the manifestation of energy in the form of heat. In all materials the atoms that make up their molecules are in continuous motion, either moving or vibrating. This movement of the particles implies that the atoms have a certain kinetic energy that we call heat, thermal energy or heat energy.
In a way, calorific energy is the internal energy of a body. The internal energy of a thermodynamic system can be changed in two ways: by doing work on the system and by exchanging heat with the environment. The energy that the body receives or loses in the process of exchanging heat with the environment is called the quantity of heat or simply heat. Energy is measured in Joules (J) according to the international system. Although when it comes to calorific energy, calories (lime) are also usually used.
Electromagnetic Energy
This energy is attributed to the presence of an electromagnetic field, generated from the movement of electric and magnetic particles moving and oscillating at the same time. They are what we know as electromagnetic waves, which propagate through space and travel at the speed of light. Electromagnetic energy consists of waves of electric and magnetic fields that propagate through space, and travel at the speed of light. The space, where these waves meet, is called the electromagnetic field. The main source of electromagnetic energy is the sun, but man-made sources are responsible for large amounts of electromagnetic radiation (the so-called artificial) in our environment.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is generated to the atoms interact with each other. It can be released through breaking, which is known as fission, or by joining, which is called fusion. Nuclear energy is the energy contained in the nucleus of an atom. Atoms are the smallest particles into which a chemical element can be divided while maintaining its properties. In the nucleus of each atom, there are two types of particles, neutrons and protons. The forces that hold the particles of the nucleus together even overcoming those of electrostatic repulsion between the protons are of an unknown nature and of short-range, they only appear inside the nuclei and are called nuclear forces. The energy accumulated by these is called binding energy.
Electricity: The Best kind of Energy?
Electricity has become the main source of light, heat and power used in the modern world, being a fundamental input used by 79% of companies, representing 40% of their production costs. Practically, a good part of the daily activities we perform require the availability of continuous and uninterrupted electricity. Banks, hospitals, corporate companies, in addition to small, medium and large industries, necessarily depend on electricity to fulfil their service hours.
Failures in this power supply can cause irreparable damage. Can we imagine a hospital, data centre, pharmaceutical industry or financial institutions operating without electricity? It would be incalculable damage, wouldn’t it? We are dealing with situations where a minute without power makes all the difference.
However, in the last three years, government policy has had an impact on the average cost for the industry of 59.3%. The unfavourable economic situation coupled with the real increase in the price of electricity in recent years contributed even more to the fall in industrial production and the reduction of national competitiveness. It cannot be hidden that the generation of electric energy causes concern to environmental sustainability.
Conservation Of Energy
In the scientific sense, the term energy conservation refers to the Principle of Physics which establishes that the total energy of the universe is constant, for any closed system. In this way, energy can only change shape: kinetic energy turns into potential energy, potential energy turns into kinetic energy, internal energy turns into heat or work. Thus, energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Energy Conservation Importance
In the technical terminology of the Engineering area, the term energy conservation refers to techniques and procedures that aim to reduce waste and inefficient use of energy, mainly electrical, without compromising comfort and/or production. In general, the term conservation is linked to the rational use of energy.
This technological area has emerged, mainly after the oil crisis in the 1970s, when the increase in the prices of this input substantially changed the stability of the strategies for obtaining the necessary resources to guarantee the sustainability of the development process.
The importance of the subject emerges from the analysis of the world energy scenario, where it is observed that, as a fundamental input, there is a direct relationship between human development and energy consumption (75% of the world population lives in developing countries with a significant repressed demand) and that the increase in energy consumption, based on current models, implies a series of investments that can result in environmental degradation (pollution, acid rain, destruction of the ozone layer).
In this way, develop ways to guarantee the energy needed for basic needs as well as to improve living standards, according to rational and adequate criteria, it is a fundamental part of the sustainable development process.
Non-Renewable and Renewable and Energy
Renewable Energy
Renewable energies are those that regenerate spontaneously or through human intervention. They are considered clean energies, because the residues left in nature are zero.
Some examples of Renewable Energies are:
- Hydroelectric – originated by the force of the water in the rivers;
- Solar – obtained by the heat and sunlight;
- Wind – derived from the strength of the winds,
- Geothermal – comes from the heat of the earth’s interior;
- Biomass – from organic materials;
- Seas and Oceans – natural wave strength;
- Hydrogen – comes from the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen that releases energy.
Non-Renewable Energies
Non-renewable energies are those that, once depleted, can no longer be regenerated, as it takes a long time for their formation in nature.
Despite being found in nature in large quantities, they have finite reserves. They are considered polluting energies, because their use causes damage to the environment.
Examples of Non-Renewable Energy Types:
Fossil fuels : Fossil fuels are raw materials for energy production. They are non-renewable natural resources, originated from organic remains accumulated in the earth’s crust over millions of years, such as oil, coal, shale and natural gas;
Nuclear Energy : Nuclear or atomic energy is the energy produced in thermonuclear plants, which use uranium and other elements, as fuel which needs uranium and thorium to be produced.
Home Uses of Energy Types
When considering the need to save energy at home, then the main focus should be on heating and cooling. They are the main uses of energy. Also the heating of the water involves a considerable use of energy, as well as the cooking process with surface units and ovens. The use of energy in a refrigerator is important.
The lighting process of an entire house becomes a significant energy consumption. Electronic devices generally use a small amount of energy, and are not a significant part of energy consumption. Although the energy consumption is measured in toe or ktoe, in reality, the domestic sector uses many different types of fuels, some from oil, but not others.
Energy consumption
Electricity accounts for almost 40% of energy consumption in homes. And electricity, in turn, is produced in thermal plants, nuclear and renewables (mainly hydro and wind). Within this 40% of the total energy consumed that represents electrical energy. It should be noted that 40% of its production came from renewable energy and 60% from non-renewable. A tiny percentage comes from photovoltaic panels, despite being the most versatile use of all and used for all kinds of applications.
Liquefied petroleum gases, butane and propane, account for 6.5% of the total. Heating, hot water processing, and kitchens all use them.
Solid fuels include charcoal and wood. They are almost entirely used for heating and make up a small percentage of overall consumption (0.5 per cent). Natural gas is the fastest-growing type of domestic energy. It accounts for 25% of demand and is used in the same ways as liquefied petroleum gases.
Diesel C accounts for slightly more than 10% of consumption. It is solely for the purpose of providing heat and hot water.
Solar thermal energy (solar panels to produce hot water) accounts for a very small percentage of total consumption (1.6%). However, it seems to be growing. It is certainly an ideal type of energy for certain applications in the domestic sector.
Finally, biomass represents 16.4% of total energy consumption in homes.
Conclusion
The natural resources of our planet are finite, that is, they will end one day. Even so, we live as if this is not an imminent reality. What world do you want to leave for your children and grandchildren? By not saving energy and natural resources, you are actively contributing to the destruction of the planet. Therefore, even though the individual contribution is relatively small in relation to the whole. Striving to change habits can make a huge difference in natural resources preservation and in guaranteeing a cleaner and more.